Quick facts
Common names - Winter moth, Mottled umber moth and March moth
Scientific names - Operophtera brumata, Erannis defoliaria, Alsophila aescularia
Plants affected - Fruit trees, oak, sycamore, hornbeam, Sorbus spp., roses and many other deciduous trees and shrubs
Main symptoms - Holes eaten in leaves, blossom and apple fruitlets
Most active - Bud burst to early June
What are winter moth caterpillars?
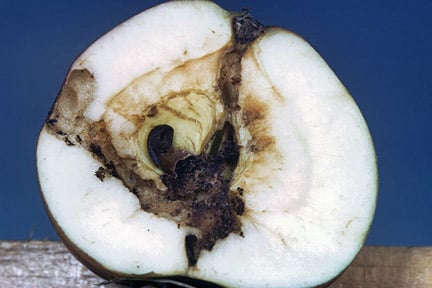
Winter moth caterpillars eat holes in the leaves, blossom and developing of many fruit trees, ornamental trees and shrubs in early spring. Severe attacks can weaken young trees. Extensive damage to fruit trees can affect crop yield and quality.
Winter moth is a name that can be used for a number of species that have adult moths that emerge and lay eggs between November and April. These moths all have wingless females that emerge from pupae in the soil and crawl up trunks to lay eggs on branches. The most important are the winter moth (Operophtera brumata), mottled umber moth (Erannis defoliaria) and March moth (Alsophila aescularia). The caterpillars of these moths hatch in the spring as are opening and they feed on most types of fruit tree and many trees and shrubs. The main fruit tree host are apples, pears, plums and cherries. Many ornamental trees are also hosts, including oak, sycamore, hornbeam, beech, dogwoods, hawthorns, Sorbus, roses, hazels and elms.
Symptoms
You may see the following symptoms:
- Winter moth caterpillars feeding is usually first noticed in spring when emerging leaves are eaten
- Feeding damage can be particularly noticeable in mid-summer when the leaves are fully expanded and the small holes made during the spring have enlarged with leaf growth, at which point the caterpillars have left the tree
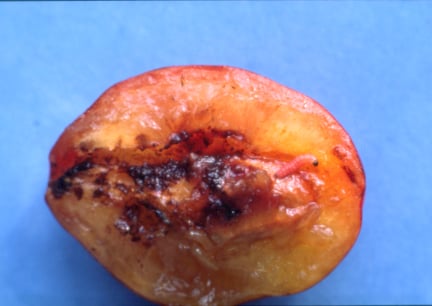
- Blossom and developing can also be damaged
- Early damage on apple fruitlets can cause a deep cleft in the side of the fruits to develop by the time they have reached full size in late summer

Management
On non fruiting trees these caterpillars can be tolerated as any leaf damage does not affect the long term health of the tree. In addition many birds, especially tits, rely on these caterpillars to rear their chicks during the spring.
- Where possible tolerate populations of winter moth caterpillars, as moths are an important part of the garden ecosystem
- Encourage predators and other natural enemies in the garden such as birds, hedgehogs and ground beetles. These caterpillars are an important food source for nesting birds
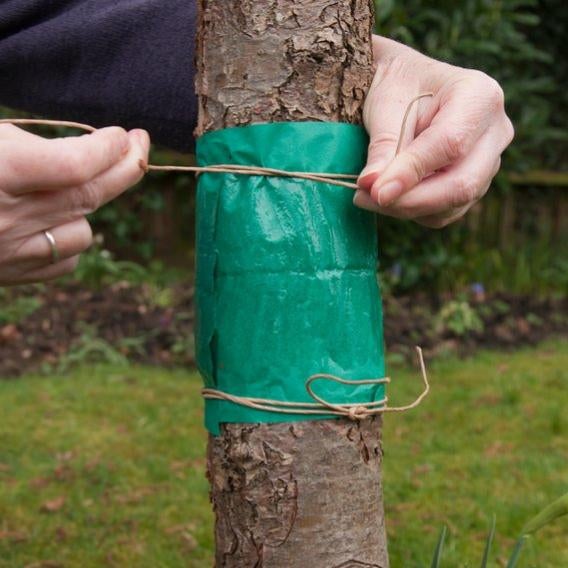
- Egg laying on fruit trees can be reduced by placing a sticky grease band or barrier glue around the trunk and tree stake (if present) in October to intercept the wingless females. This needs to be kept sticky and free of detritus until mid-April. Grease bands and barrier glues must not include glues that are strong enough to entangle larger animals such as birds, bats or mice. Grease bands and barrier glues are indiscriminate and can capture any that tries to cross them. They should therefore be used sparingly, for example only where winter moths have been a problem in the past, to reduce any negative effects on non-target animals such as earwigs. It is also important that they are only kept in place from autumn until spring when the adult winter moths may be active.
Biology
Wingless female winter moths emerge from pupae in the soil during November to April and crawl up trunks to lay eggs on the branches.
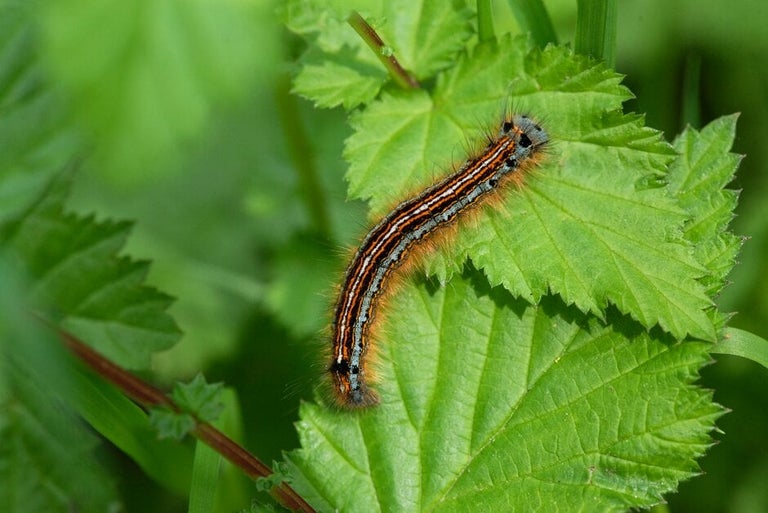
Eggs hatch at burst and the pale green looper-type caterpillars emerge and start feeding. The caterpillars are up to 25 mm (about 1 in) long and complete their feeding by early June. They then go down into the soil where they pupate.
In some years oaks and other trees are largely defoliated during the spring by the caterpillars of winter moth and other species. Such trees will survive and produce more leaves during the summer with no long term effects on their health.